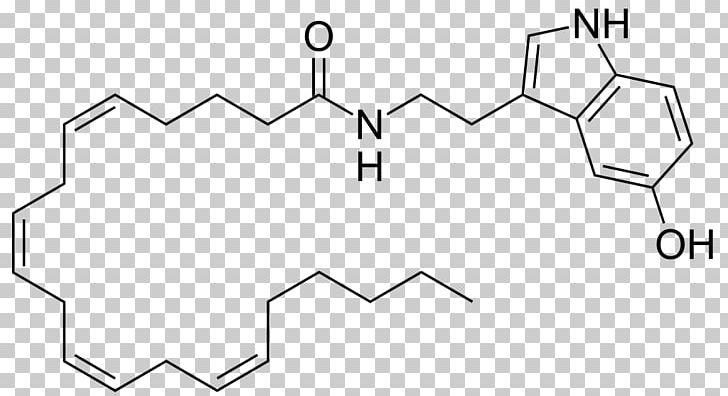
Arachidonoyl serotonin (N-arachidonoyl-serotonin, AA-5-HT) is an endogenous lipid signaling molecule. It was first described in 1998 as being an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). In 2007, it was shown to have analgesic properties and to act as an antagonist of the TRPV1 receptor. In 2011, it was shown to be present in the ileum and jejunum of the gastrointestinal tract and modulate glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion. In addition to this, in 2016, AA-5-HT was also found to affect the signaling mechanisms responsible for anxiety, by inhibiting dopamine release from the Basolateral amygdala following fear behavior. In 2017, AA-5-HT was tested in its effects on the sleep wake cycle, where it was found to affect the sleep homeostasis when used in conjunction with molecules and chemicals that affect wake-related neurotransmitters.
See also
- Endocannabinoid system
References